NOIP2011普及组 T4 表达式的值¶
0.前言¶
- 先具备表达式树的建树基础
- 这道题目正解是用一个符号栈、一个数字栈进行模拟,可以使用模板代码实现
- 更为重要的是思考这道题目,如何建树,跑递归,做树形dp,实现,这时会发现只有80pts
- 有两个点是TLE,T在了建树的过程时间复杂度是O(n^2),这个时候,搞一下笛卡尔树,O(n)时间复杂度建树
- 更为重点的是,往上的题解有很多,有份研究报告,值得我们学习,分享在这里
1.基础知识,表达式树,紫书P353¶
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int lch[N], rch[N], idx;
char op[N];
char s[N];
int root;
int build(char *s, int x, int y){
int c1 = -1, c2 = -1, p = 0;
int u;
if (y - x == 1){
u = ++idx;
lch[u] = rch[u] = 0, op[u] = s[x];
return u; //返回结点编号
}
for (int i = x; i < y; i++){
if (s[i] == '(') p++;
if (s[i] == ')') p--;
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-')
if (!p) c1 = i;
if (s[i] == '*' || s[i] == '/')
if (!p) c2 = i;
}
if (c1 < 0) c1 = c2;
if (c1 < 0) return build(s, x + 1, y - 1);
u = ++idx;
lch[u] = build(s, x, c1);
rch[u] = build(s, c1 + 1, y);
op[u] = s[c1];
return u;
}
void dfs(int u){
if (lch[u] == 0 && rch[u] == 0){
cout << op[u];
return ;
}
dfs(lch[u]);
cout << op[u];
dfs(rch[u]);
}
int dfs2(int u){
if (lch[u] == 0 && rch[u] == 0){
return op[u] - '0';
}
int a = dfs2(lch[u]);
int b = dfs2(rch[u]);
if (op[u] == '+') return a + b;
if (op[u] == '-') return a - b;
if (op[u] == '*') return a * b;
if (op[u] == '/') return a / b;
}
int main(){
scanf("%s", s);
root = build(s, 0, strlen(s));
//dfs(root);
cout << dfs2(root) << '\n';
return 0;
}
// 用这个代码,我们可以学习如何建树,适用这种表达式的题目
// 熟练使用递归
2.正解,一个符号栈,一个数字栈¶
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mod = 10007;
stack<vector<int> > num;
stack<char> op;
int n;
string s;
void eval(){
vector<int> b = num.top(); num.pop();
vector<int> a = num.top(); num.pop();
char c = op.top(); op.pop();
if (c == '*') num.push({(a[0]*b[0] + a[0]*b[1] + a[1]*b[0])%mod, a[1]*b[1]%mod});
else num.push({a[0]*b[0]%mod, (a[0]*b[1] + a[1]*b[0] + a[1]*b[1])%mod});
}
int main(){
map<char, int> pr;
pr['('] = 0, pr['+'] = 1, pr['*'] = 2;
cin >> n >> s;
num.push({1, 1});
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
char c = s[i];
if (c == '('){
op.push(c);
}
else if (c == ')'){
while (op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
}
else{
while (op.size() && pr[op.top()] >= pr[c]) eval();
num.push({1, 1});
op.push(c);
}
}
while (op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top()[0] << '\n';
return 0;
}
// 这个代码中,符号优先级的表示,eval()函数的写法,是通用的
3.开始研究建树,做树形dp¶
// 80pts
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 10007;
int lch[N], rch[N], idx;
char op[N];
char s[N];
int root, n;
int build(char *s, int x, int y){
int c1 = -1, c2 = -1, p = 0;
int u;
if (y - x == 0){
u = ++idx;
lch[u] = rch[u] = -1;
return u; //返回结点编号
}
for (int i = x; i < y; i++){
if (s[i] == '(') p++;
if (s[i] == ')') p--;
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-')
if (!p) c1 = i;
if (s[i] == '*' || s[i] == '/')
if (!p) c2 = i;
}
if (c1 < 0) c1 = c2;
if (c1 < 0) return build(s, x + 1, y - 1);
u = ++idx;
lch[u] = build(s, x, c1);
rch[u] = build(s, c1 + 1, y);
op[u] = s[c1];
return u;
}
void dfs(int u){
if (lch[u] == 0 && rch[u] == 0){
cout << op[u];
return ;
}
dfs(lch[u]);
cout << op[u];
dfs(rch[u]);
}
vector<int> dfs2(int u){
if (lch[u] == -1 && rch[u] == -1){
return {1, 1};
}
vector<int> a = dfs2(lch[u]);
vector<int> b = dfs2(rch[u]);
if (op[u] == '+') return {a[0]*b[0]%mod, (a[0]*b[1] + a[1]*b[0] + a[1]*b[1])%mod};
if (op[u] == '*') return {(a[0]*b[0] + a[0]*b[1] + a[1]*b[0])%mod, a[1]*b[1]%mod};
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
getchar();
scanf("%s", s);
root = build(s, 0, n);
//dfs(root);
vector<int> ret = dfs2(root);
cout << ret[0] << '\n';
return 0;
}
// vector<int> dfs2(int u),这个函数返回传递的是[0的方案数, 1的方案数]
// TLE在哪了呢? 传递vector会耗时吗
// 建树的过程是o(n^2)的,80pts
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 10007;
int lch[N], rch[N], idx;
char op[N];
char s[N];
int f[N][2];
int root, n;
int build(char *s, int x, int y){
int c1 = -1, c2 = -1, p = 0;
int u;
if (y - x == 0){
u = ++idx;
lch[u] = rch[u] = -1;
return u; //返回结点编号
}
for (int i = x; i < y; i++){
if (s[i] == '(') p++;
if (s[i] == ')') p--;
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-')
if (!p) c1 = i;
if (s[i] == '*' || s[i] == '/')
if (!p) c2 = i;
if (!p && (c1 != -1 || c2 != -1)) break;
}
if (c1 < 0) c1 = c2;
if (c1 < 0) return build(s, x + 1, y - 1);
u = ++idx;
lch[u] = build(s, x, c1);
rch[u] = build(s, c1 + 1, y);
op[u] = s[c1];
return u;
}
void dfs(int u){
if (lch[u] == 0 && rch[u] == 0){
cout << op[u];
return ;
}
dfs(lch[u]);
cout << op[u];
dfs(rch[u]);
}
void dfs2(int u){
if (lch[u] == -1 && rch[u] == -1){
f[u][0] = f[u][1] = 1;
return ;
}
int a = lch[u], b = rch[u];
dfs2(a);
dfs2(b);
if (op[u] == '+'){
f[u][0] = f[a][0]*f[b][0]%mod;
f[u][1] = (f[a][0]*f[b][1] + f[a][1]*f[b][0] + f[a][1]*f[b][1])%mod;
}
if (op[u] == '*'){
f[u][0] = (f[a][0]*f[b][0] + f[a][0]*f[b][1] + f[a][1]*f[b][0])%mod;
f[u][1] = f[a][1]*f[b][1]%mod;
}
return ;
}
int main(){
freopen("P1310_2.in", "r", stdin);
scanf("%d", &n);
getchar();
scanf("%s", s);
root = build(s, 0, n);
//dfs2(root);
//cout << f[root][0] << '\n';
return 0;
}
// void dfs2(int u) 改成了void类型,用f[N][2]来维护方案数
// 依然超时,研究发现是因为建树的过程dfs() 每一次执行都是O(n)的,n个点,O(n^2)
4.笛卡尔树,建树O(n)¶
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 10007;
struct node{
int lch, rch;
char op;
}tree[N * 2];
char s[N];
int f[N][2], w[N], idx, n, root;
int st[N], k, top = -1;
void build(){
int p = 0; //维护由多少个括号包围
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if (s[i] == '(') p++;
if (s[i] == ')') p--;
if (s[i] == '+'){
w[++idx] = p * 2 + 1; // 维护优先级
tree[idx].op = s[i];
}
if (s[i] == '*'){
w[++idx] = p * 2 + 2;
tree[idx].op = s[i];
}
}
// 笛卡尔建树模板
for (int i = 1; i <= idx; i++){
k = top;
while (k >= 0 && w[st[k]] > w[i]) k--;
if (k != -1) tree[st[k]].rch = i;
if (k < top) tree[i].lch = st[k + 1];
st[++k] = i;
top = k;
}
root = st[0];
}
void dfs(int u){
if (u == 0) return ;
int a = tree[u].lch, b = tree[u].rch;
char op = tree[u].op;
if (a != -1) dfs(a);
if (b != -1) dfs(b);
if (op == '+'){
f[u][0] = f[a][0]*f[b][0]%mod;
f[u][1] = (f[a][0]*f[b][1] + f[a][1]*f[b][0] + f[a][1]*f[b][1])%mod;
}
if (op == '*'){
f[u][0] = (f[a][0]*f[b][0] + f[a][0]*f[b][1] + f[a][1]*f[b][0])%mod;
f[u][1] = f[a][1]*f[b][1]%mod;
}
return ;
}
int main(){
//freopen("P1310_2.in", "r", stdin);
scanf("%d", &n);
getchar();
scanf("%s", s + 1);
build();
f[0][0] = f[0][1] = 1;
dfs(root);
cout << f[root][0] << '\n';
return 0;
}
// 这样就可以AC了
5.分享一个特别有启发的研究报告¶
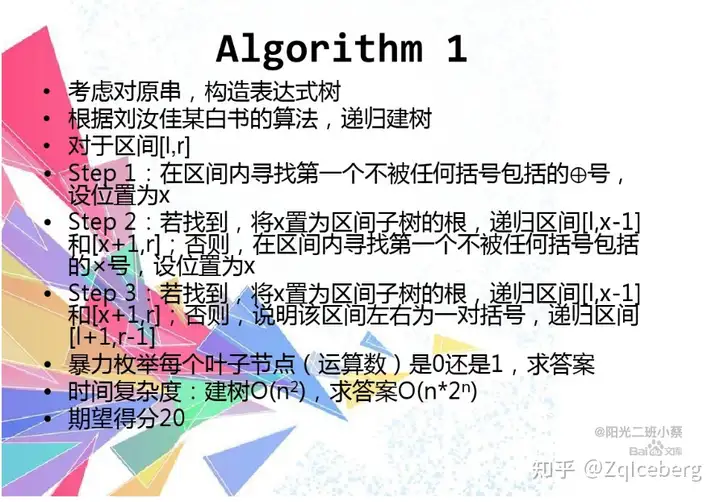
NOIP2011Junior表达式的值(非题解方法) - 百度文库









说在后面
- 有好的灵感,不要轻易放过
- 可能当初想到时候,水平有限实现不出来,功力深了后,可以实践灵感
6.关于笛卡尔树的资料¶
7.总结¶
写这道题目的时候,先是发现有几道类似的表达式的题目,一起看了看,发现这个正解,我并不会做,看题解的时候,发现建树的方法繁琐,但我并不会,我就研究一下建树,发现会T,怎么不会T呢,然后又遇见了笛卡尔树和RMQ,我就又学习了一遍,发现虽然还是不会,但是笛卡尔的建树过程,还是很清晰了,(每次我们插入的元素,必然在树的右链的末端。每个结点最多进出右链一次,用一个栈来维护这个过程)