拓扑序¶
前置知识¶
建图,BFS
目标¶
拓扑序的模板题
What¶
在计算机科学领域,有向图的拓扑排序或拓扑测序是对其顶点的一种线性排序,使得对于从顶点 u 到顶点 v 的每个有向边 uv,u 在排序中都在 v 之前。
例如,图形的顶点可以表示要执行的任务,并且边可以表示一个任务必须在另一个任务之前执行的约束;在这个应用中,拓扑排序只是一个有效的任务顺序。
当且仅当图中没有定向环时(即有向无环图),才有可能进行拓扑排序。
任何有向无环图至少有一个拓扑排序。已知有算法可以在线性时间内,构建任何有向无环图的拓扑排序。
在图论中,由一个有向无环图的顶点组成的序列,当且仅当满足下列条件时,才能称为该图的一个拓扑排序(英语:Topological sorting): 1、序列中包含每个顶点,且每个顶点只出现一次; 2、若A在序列中排在B的前面,则在图中不存在从B到A的路径。
Topological sorting拓扑序,看名称有一个sorting的单词,但并不是和快排是一块的东西。
场景:拓扑序,解决具有层级性的问题。 在某校的选课系统中,存在这样的规则:每门课可能有若干门先修课,如果要修读某一门课,则必须要先修读此课程所要求的先修课后才能修读。假设一个学生同时只能修读一门课程,那么,被选课系统允许的他修完他需要所有课程的顺序是一个拓扑序。 在这个例子中,每一门课程对应有向图中的一个顶点,每一个先修关系对应一条有向边(从先修课指向需要先修课的课)。
A topological sort is an ordering of the nodes of a directed graph such that if there is a path from node a to node b, then node a appears before node b in the ordering. For example, for the graph one topological sort is [4,1,5,2,3,6]:
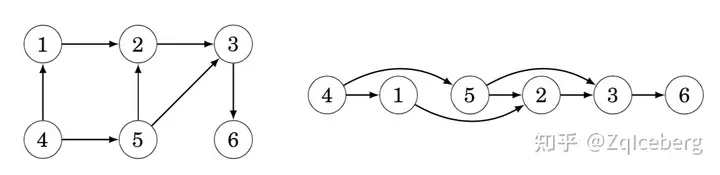
An acyclic(无环的) graph always has a topological sort. However, if the graph contains a cycle, it is not possible to form a topological sort, because no node of the cycle can appear before the other nodes of the cycle in the ordering. It turns out that depth-first search can be used to both check if a directed graph contains a cycle and, if it does not contain a cycle, to construct a topological sort.
topsort就是有向图的宽度优先遍历的应用 拓扑序,不唯一 如要要字典序最小的拓扑序,在遍历入度为0的点的时候,从1开始遍历,并入队 有明显【层级关系】的问题,可以考虑用topsort()模型
How¶
卡恩算法
L ← 包含已排序的元素的列表,目前为空
S ← 入度为零的节点的集合
当 S 非空时:
将节点n从S移走
将n加到L尾部
选出任意起点为n的边e = (n,m),移除e。如m没有其它入边,则将m加入S。
重复上一步。
如图中有剩余的边则:
return error (图中至少有一个环)
否则:
return L (L为图的拓扑排序)
例题¶
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110, M = 110 * 110;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int n, in[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void topsort()
{
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if(!in[i]) q.push(i);
while (!q.empty()){
int t = q.front(); q.pop();
printf("%d ", t);
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
in[j]--;
if (!in[j]) q.push(j);
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x;
while (cin >> x && x){
add(i, x);
in[x]++;
}
}
topsort();
puts("");
return 0;
}
题单¶
1352:【例4-13】奖金 1395:烦人的幻灯片(slides) P1347 排序 1964:【13NOIP普及组】车站分级
总结¶
拓扑序,在考纲里是提高组的,但我认为可以在普及组阶段直接学习,练习对图的理解和掌握。