并查集
Union-find structure 并查集(DSU)¶
为什么要用并查集¶
一开始有一些互相不认识的人,现在每天逐渐有一对对的人互相认识。
然后我想知道,两个人有没有可能通过朋友介绍而认识。
并查集¶
A union-find structure maintains a collection of sets. The sets are disjoint, so no element belongs to more than one set. Two *O*(log*n*)** time operations are supported: the unite operation joins two sets, and the find operation finds the representative of the set that contains a given element.
structure数据结构
In a union-find structure, one element in each set is the representative of the set, and there is a chain from any other element of the set to the representative. For example, assume that the sets are {1,4,7}, {5} and {2,3,6,8}:
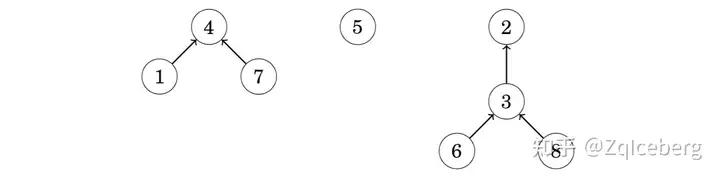
In this case the representatives of the sets are 4, 5 and 2. We can find the representative of any element by following the chain that begins at the element. For example, the element 2 is the representative for the element 6, because we follow the chain 6 → 3 → 2. Two elements belong to the same set exactly when their representatives are the same.
Two sets can be joined by connecting the representative of one set to the representative of the other set. For example, the sets {1,4,7} and {2,3,6,8} can be joined as follows:
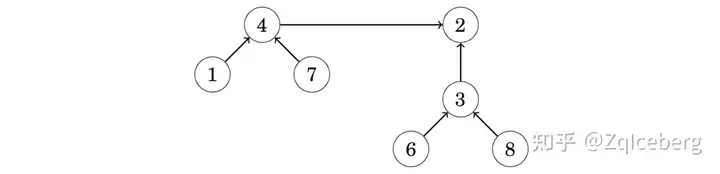
The resulting set contains the elements {1,2,3,4,6,7,8}. From this on, the element 2 is the representative for the entire set and the old representative 4 points to the element 2.
The efficiency of the union-find structure depends on how the sets are joined. It turns out that we can follow a simple strategy: always connect the representative of the smaller set to the representative of the larger set (or if the sets are of equal size, we can make an arbitrary choice). Using this strategy, the length of any chain will be *O*(log*n*)**, so we can find the representative of any element efficiently by following the corresponding chain.
// 初始化
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
// 返回x的祖宗结点+路径压缩
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 补充,下面这样写,就没有实现路径压缩
int find(int x){
if (p[x] != x) return find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 合并
p[find(a)] = find(b);
// 或者
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa != pb) p[pa] = pb;
// 另外一份模板
// the array link contains for each element the next element in the chain
// or the element itself if it is a representative,
// and the array size indicates for each representative the size of the corresponding set
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) link[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) size[i] = 1;
void unite(int a, int b) {
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
if (size[a] < size[b]) swap(a,b);
size[a] += size[b];
link[b] = a;
}