结构体¶
结构体¶
结构体是一种自定义的数据类型,将不同类型的数据成员组合在一起,形成一个包含多个相关数据字段的复合数据类型。
结构体能显式地将成员变量捆绑在一起展示,更直观
访问结构体的成员变量¶
结构体变量名.成员变量名
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct stu{
string name;
int id;
int chinese, math;
};
int main()
{
// 结构体变量定义时,直接对成员变量赋值
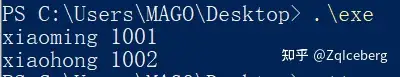
stu A = {"xiaoming", 1001, 90, 95};
// 先定义,再给成员变量赋值
stu B;
B.name = "xiaohong", B.id = 1002, B.chinese = 99, B.math = 92;
// 输出
cout << A.name << ' ' << A.id << '\n';
cout << B.name << ' ' << B.id << '\n';
return 0;
}
结构体的构造函数¶
构造函数,就是结构体的初始化
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int x, y;
node(int x = 0, int y = 0): x(x), y(y){} // 成员初始化表达式列表
};
int main(){
node(2, 3);
return 0;
}
// 构造函数的使用,在一些复杂的代码中,优势就体现出来了。简洁,好写。
// 构造函数的写法,经过查资料,至少有两种写法,上面这种是稳定性更好的。
// 但是让人感觉很陌生的写法
// 多背几遍就是了
结构体的自定义排序(重点)¶
sort() 函数默认是从小到大排序,但是结构体里面有很多元素,怎么个排序法呢,需要我们去定义它。
什么是多关键字的自定义排序
就像操作 Excel 表格的时候,有年龄、身高两个关键字。
我们排序就要看年龄大的在前面,如果年龄相同,身高小的在前面,类似这样的排序规则
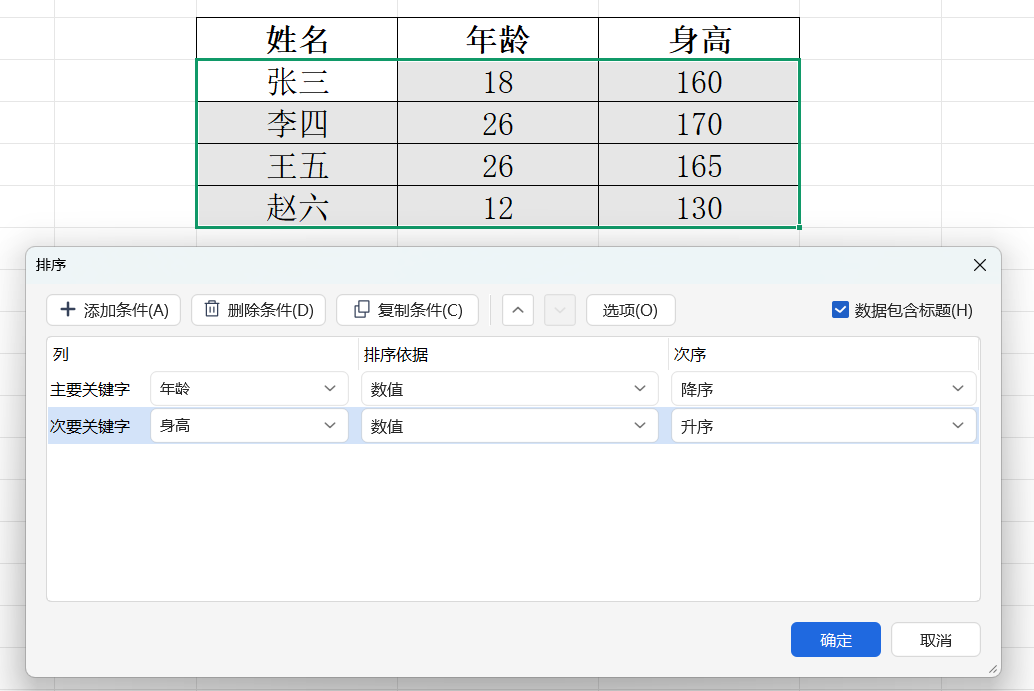
完成排序后,如下:
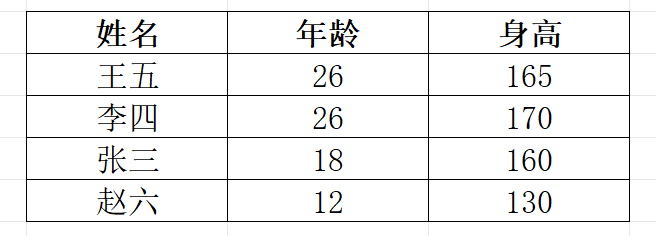
使用
cmp函数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
struct node{
int x, y;
node(int x = 0, int y = 0): x(x), y(y){}
}a[N];
int n;
bool cmp(node a, node b){
if (a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y;
return a.x < b.x;
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y;
sort(a, a + n, cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << a[i].x << ' ' << a[i].y << '\n';
return 0;
}
使用重载小于符号
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
struct node{
int x, y;
node(int x = 0, int y = 0): x(x), y(y){}
bool operator< (const node& W)const{
if (x == W.x) return y < W.y;
return x < W.x;
}
}a[N];
int n;
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y;
sort(a, a + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << a[i].x << ' ' << a[i].y << '\n';
return 0;
}